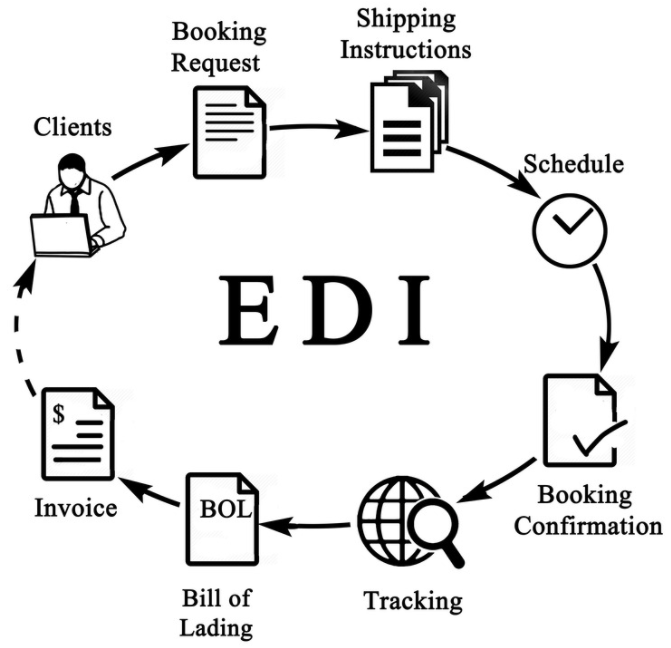
Save time by letting systems talk with each other
Oh tech acronyms. We hear them all the time, and most of the time we nod along while in the back of your mind you’re thinking “what the heck are they talking about?!?”. In this tech talk post, we’re going to explain—in plain english—what Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is, what it does to help your business, and how you’re probably using it everyday and don’t even know it.
Stop Being an Information Middleman
You know in the movies when someone says “I’ll have my people talk to your people to work out the details?”. One person tells their assistant to call someone else’s assistant to work out whatever it is that needs doing.
Simple, fast, and efficient.
That, for all intents and purposes, is what EDI is. It’s a way for two computer systems to exchange information and get something done for you that you were doing manually before.
EDI Basics has some handy images of life before EDI and life after EDI to illustrate how things work at a high level.
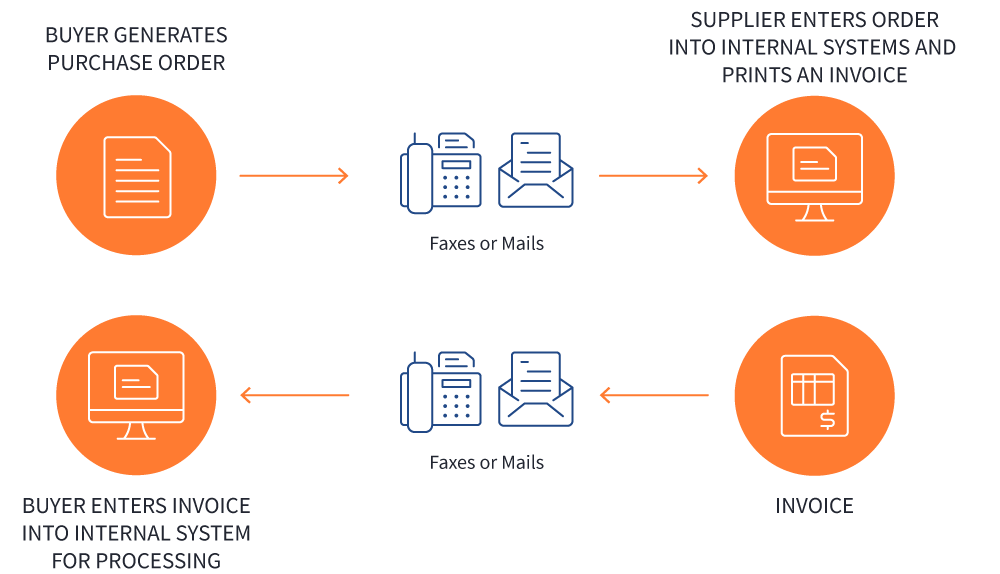
Let’s take the scenario for a customer paying you for hauling a load. First, you go into your invoicing system and generate an invoice. You fax, email, or mail the invoice to the customer. Then the customer receives the invoice and inputs it into their accounting system to pay you.
We’ve done this thousands of times. And we know what can go wrong. The fax gets lost. The email is missed or goes to junk. The invoice is entered into the customer’s accounting system wrong. Or there is a delay in processing it because people are out or on vacation.
There are a lot of places things can go wrong when you rely on people to connect the data dots for you.
We’ve all seen it happen. And beyond the time it took to create, send, and record that invoice (on both sides of the equation), now you have to follow up with the customer. Not a great use of anyone’s time.
EDI makes the whole process smooth, efficient, and painless.
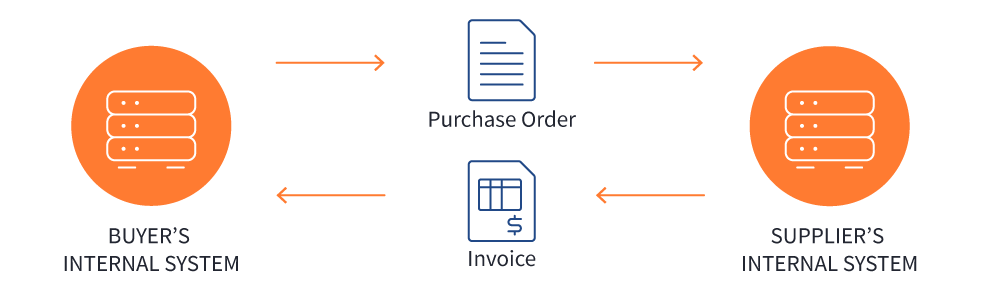
It goes something like this:
You’ve set up with your customer how your systems can talk to their systems. When you generate an invoice and send it, the information is automatically entered into their accounting system. You get confirmation the information is sent and you’re done.
There is no one creating invoices to email on one side or a person receiving and entering the invoice on the other. It’s all automatic.
If the systems can do it, the entire work order, booking, invoicing, and payment can be handled this way. Customers book loads with you, you see and approve them, log them into the TMS, and then invoice your customer.
Every step of the way, people know what’s going on. Load booked and accepted. Driver dispatched. Load delivered. Invoice generated. Invoice received. Payment sent. Done.
So how does it all work?
The Nuts and Bolts of EDI
When you send an email, computers across the internet talk to each other to get your email where it’s supposed to go. This works because all email systems have a standardized language they work with. Each part of your email is sent a certain way each time. The to, from, subject, and message are all noted a certain way so all email servers know what do to with it.
It wasn’t always this way. Thirty-odd years ago you might have to have three or four email addresses because systems didn’t have a system to talk with each other.
The nuts and bolts—really the ones and zeros—of EDI works the same way. And it happens all the time in every business and industry you can think of. In fact when you log into your bank and pay a bill electronically, that works because of EDI.
Here’s why.
Like the email example, it all comes down to agreeing on how to describe things, connect computers, and say what needs to be done.
There are several standard for how data can be formatted and sent. Some of the most common are ANSI, EDIFACT, TRADACOMS, and ebXML. You don’t need to worry about what these are, what’s important is the role they play. EDI standards make sure there is absolutely no confusion what a piece of data is or what it means.
For example, how do you format the date? There are a lot of ways to do it, which can lead to confusion like: 02/03/2021. To some people that’s February 3rd, 2021, to other people it’s March 2nd, 2021. Which is it? Are you writing the date as month/day/year or day/month/year? EDI standards take the guesswork out. When data is sent from computer to computer the two systems already know how dates work and how they are written.
No confusion. No invoices mistakenly marked due a month later than they are supposed to be.
EDI Data Files and Translators
The magic of EDI happens in two–three steps. Let’s take the invoicing a customer example to start with.
Your TMS (transportation management system) tells you a load has been delivered to its destination by your driver and the load has been accepted by the customer. You need to invoice the customer (and pay the driver). In your TMS you click to invoice your customer. Assuming you have automatic connections set up via EDI here’s what happens next.
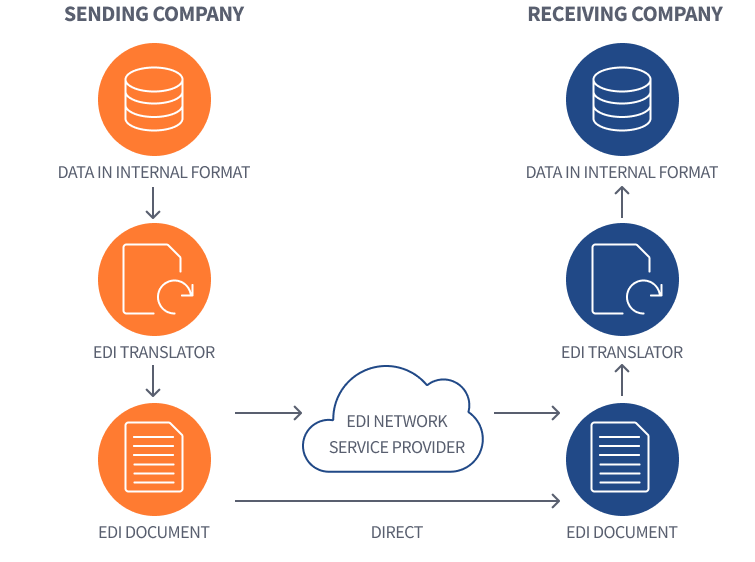
The invoice data is sent to an EDI translator module to generate a data file to sent to your customer. The data is either sent directly to your customer’s systems or via an EDI Network Provider—think of it like drayage for data.
On your customer’s side, the data file is received and goes through their EDI translator to match your data up with their data. The translators make sure all the information you sent is standardized and your data fields like date, work order number, invoice amount, will match up on the other side.
If you’ve ever imported data into Excel, it’s the same process, just automated.
Envase Makes EDI Easy
Envase is here to make your life easier and help you grow your business. We do that by helping you automate your day-to-day work as much as possible. From automated work orders to delivery tracking, invoicing to payroll—and even EDI. Envase TMS and the Envase family of solutions put you in control of your data and your business.
When you don’t have to worry about how your business is running, you can focus on one thing—growing and building your business for the future.
If you’d like to learn more how Envase TMS tackles EDI, get in touch for a free demo.